Let's find what your project needs
Emmaty’s structural engineering division excels in designing resilient, sustainable, and technically advanced infrastructure that meets both current needs and future challenges. Our team specializes in areas such as seismic, marine, and civil engineering, using materials and precision design to ensure every structure is safe, durable, and efficient. By combining creative vision with rigorous engineering principles, Emmaty delivers modular, resilient solutions that align with sustainability goals. Our approach emphasizes collaboration and innovation, ensuring that each project is tailored to the unique demands of clients and environments.
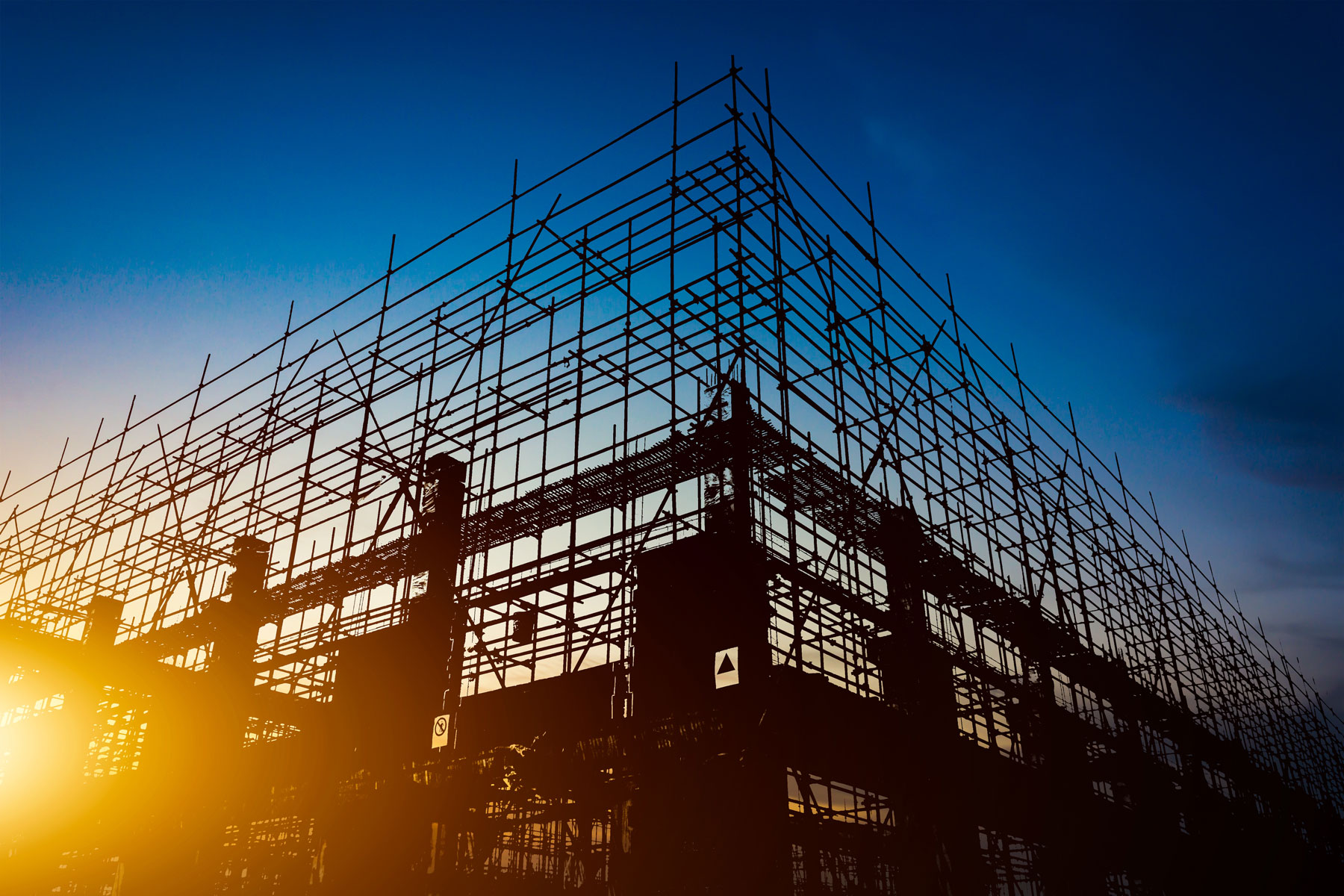

Structural Engineering
At Emmaty, structural engineering is centered on the safe, resilient, and efficient design of buildings and civil structures—including bridges, towers, industrial facilities, and critical infrastructure systems. Our team integrates principles of physics, mathematics, and material science to ensure that every structure can successfully withstand the loads and stresses it will encounter throughout its lifespan.
Emmaty’s structural engineers carefully evaluate forces such as gravity, occupancy demands, seismic activity, and wind effects, developing solutions that enhance strength, stability, and long-term performance. Through precise analysis and innovative design strategies, we create structures that are robust, dependable, and tailored to client and project requirements.
The work we deliver at Emmaty is essential in shaping structures that not only achieve architectural vision but also exceed regulatory standards, ensuring safety, reliability, and engineering excellence in every project.
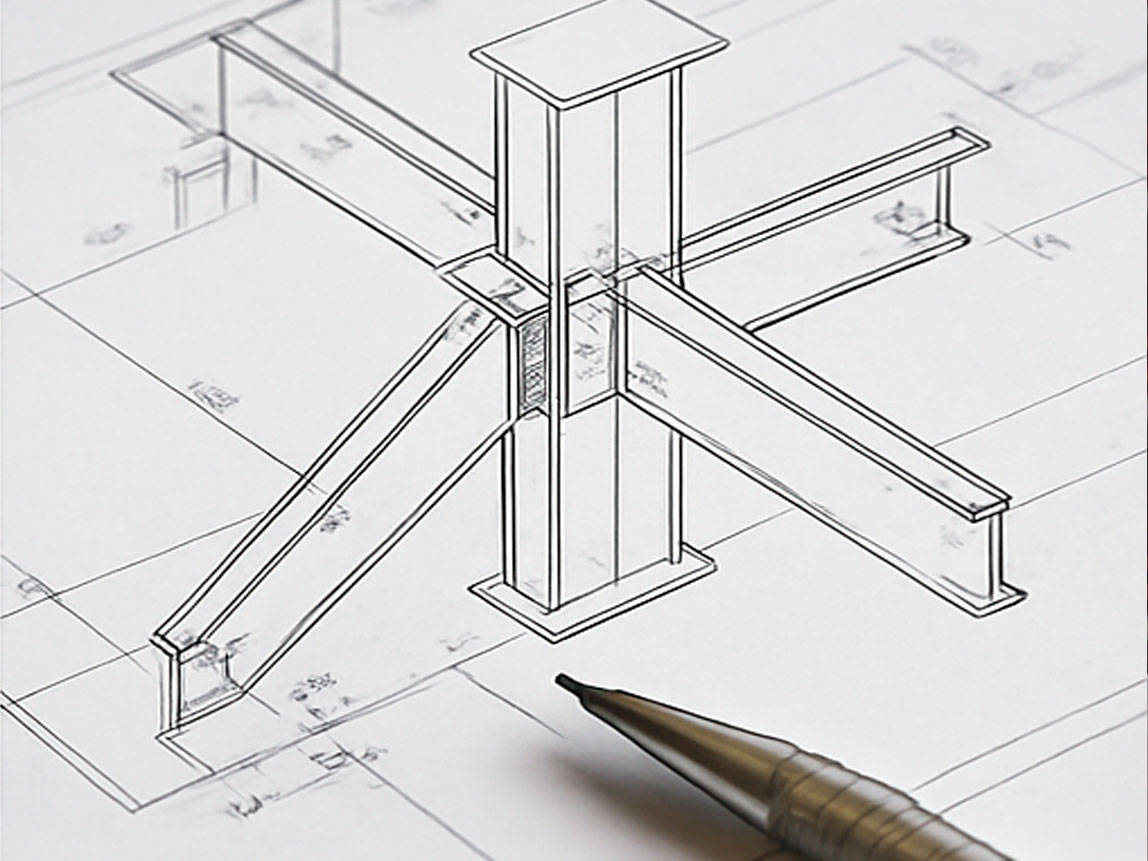
Structural Steel Detailing
At Emmaty, structural steel detailing plays a critical role in transforming engineering concepts into buildable reality. Our team prepares the detailed fabrication drawings and erection plans required for the accurate manufacturing and assembly of steel components.
This discipline serves as the essential bridge between engineering design and construction, converting structural engineering plans into precise, shop-ready documents. Emmaty’s detailing work outlines exact dimensions, material specifications, connection requirements, and welding details, giving fabricators and contractors the clarity they need to execute projects with accuracy and confidence.
By delivering high-quality, meticulously coordinated steel detailing, Emmaty enhances construction efficiency, minimizes errors, and ensures that steel structures are fabricated and erected in full alignment with design intent, project specifications, and industry standards.
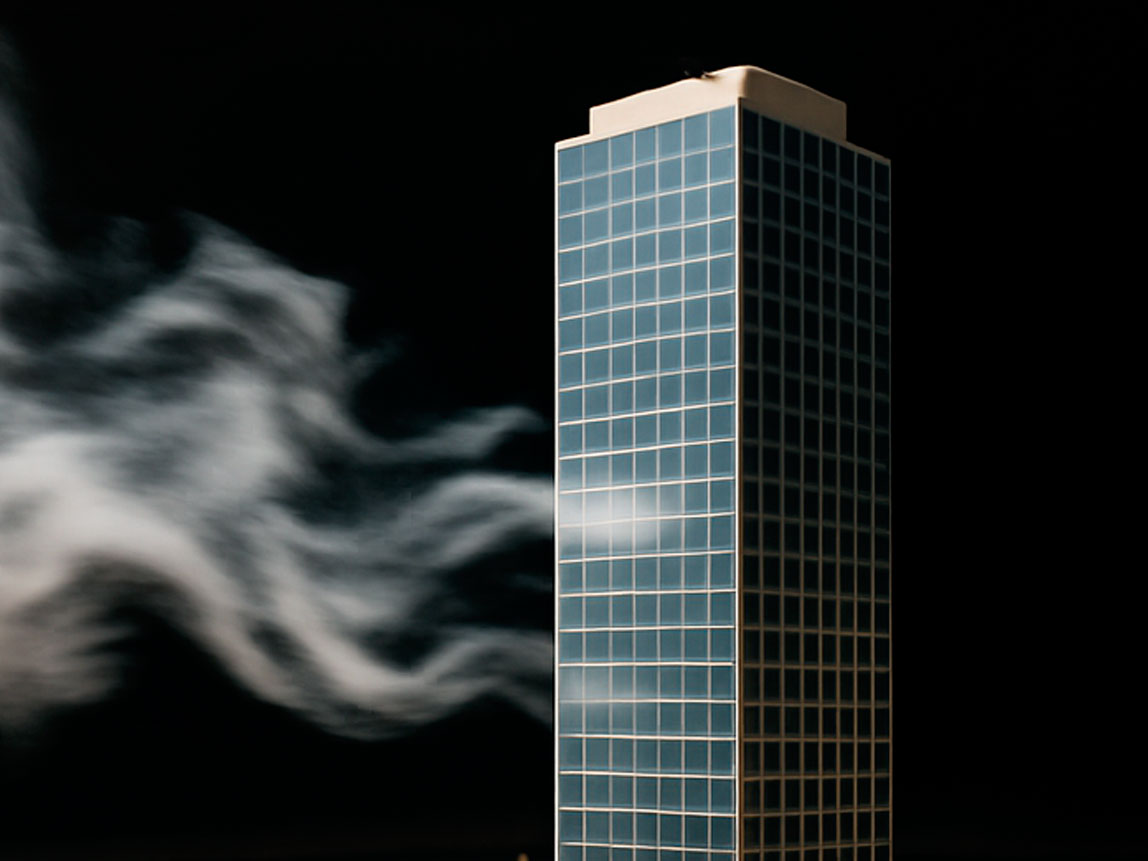

Wind Engineering & Modelling
At Emmaty, wind engineering and modelling are essential components of our approach to designing safe, resilient, and high-performing structures. This discipline focuses on understanding how wind interacts with buildings, towers, bridges, and other structures—and how these forces impact overall safety, comfort, and long-term performance.
Our engineers use advanced computational tools, simulations, and, when needed, wind tunnel testing to evaluate wind pressures, dynamic responses, and potential aeroelastic effects. This analysis is especially critical for tall, slender, or uniquely shaped structures that are more susceptible to wind-induced movement and vibrations.
By accurately modelling wind loads, Emmaty ensures that every structure we design is stable, resilient, and comfortable for occupants. Our wind engineering insights also support efficient material use and strict compliance with code requirements, contributing to smarter and more sustainable engineering outcomes.
